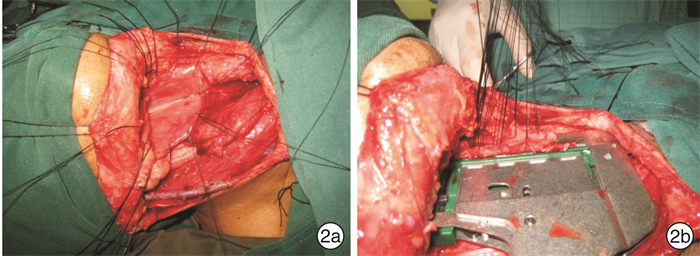
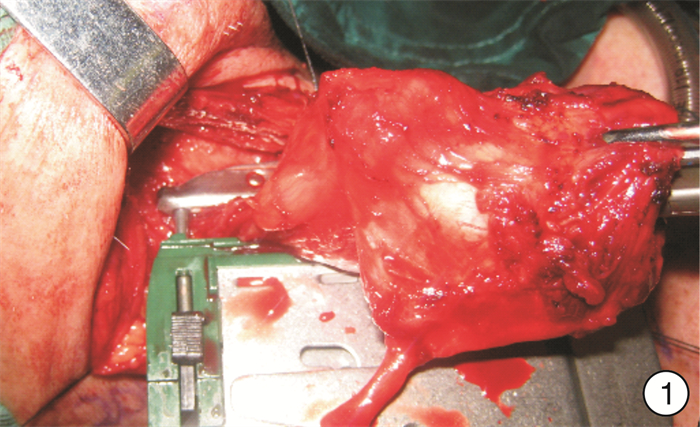
Analysis of the effect of linear stapler closure pharyngeal after total laryngectomy
-
摘要: 目的 探讨全喉切除术中线型闭合器和手工缝合关闭咽腔的疗效。方法 回顾性分析2014-12-2019-03行全喉切除术中使用线型闭合器关闭咽腔的32例患者的临床资料,其中采用密闭式技术25例(密闭式组),开放式技术7例(开放式组)。同时收集同术者于2010-01-2014-12行全喉切除术手工缝合咽腔23例(对照组)。对各组临床参数进行统计学分析。结果 密闭式组与对照组在性别、合并有糖尿病、二次手术、T分期以及手术方式上差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。而2组年龄分别为(63.60±9.46)岁和(54.35±11.13)岁、手术时间分别为(239.67±88.43)min和(474.35±140.16)min、经口进食时间分别为(12.84±3.65)min和(17.3±9.71)min、术后至出院时间分别为(15.48±3.78)d和(20.22±10.14)d、术后咽瘘发生率分别为4.0%(1/25)与26.1%(6/23),差异均有统计学意义(P<0.05)。闭合器的开放式组与对照组的性别、T分期、经口进食时间、术后出院时间、手术方式及咽瘘发生率比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),而年龄、合并有糖尿病、二次手术、手术时间比较差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。结论 采用闭合器密闭式技术能够降低咽瘘的发生率、缩短手术时间和经口进食时间,同时降低住院日。Abstract: Objective To compare the effect of closure of pharyngeal cavity with linear stapler and manual suture in total laryngectomy.Method A retrospective study was conducted on 32 patients who underwent total laryngectomy with linear stapler to close the pharyngeal from December 2014 to March 2019. Among them, 25 patients used closed technique and 7 patients used open technique. At the same time, 23 patients who underwent total laryngectomy with manual suture the pharyngeal by the same operator from January 2010 to December 2014 were collected. The clinical parameters of the two groups were compared and analyzed.Result Compared with the control group, the closed technical group had no significant difference in terms of gender, diabetes mellitus, second surgery, T stage, and surgical method(P> 0.05). While the age (63.60 ± 9.46) years and (54.35 ± 11.13) years, operation time (239.67 ± 88.43) min and (474.35 ± 140.16) min, oral feeding time (12.84 ± 3.65) min and (17.3 ± 9.71)min, hospitalization days after operation (15.48 ± 3.78) d and (20.22 ± 10.14) d, incidence of Pharygocutaneous fistula 4.0% (1/25) and 26.1% (6/23), had significant statistical differences (P < 0.05) Between two groups; Compared with the control group, the opener group had no statistically significant difference in gender, T stage, oral feeding time, hospitalization days after operation, surgical method and incidence of Pharygocutaneous fistula (P> 0.05), while there was a statistically significant difference in diabetes mellitus, second surgery, and operation time (P < 0.05).Conclusion The linear stapler closed closure technique can reduce the incidence of Pharygocutaneous fistula, shorten the operation time and oral feeding time, and reduce the length of hospital stay.
-
Key words:
- laryngectomy /
- linear stapler /
- linear /
- pharygocutaneous fistula
-

-
表 1 密闭式组和对照组临床资料比较
密封式组 对照组 统计值 P 性别 0.479 男 25(100.0) 22(95.7) 女 0(0) 1(4.3) 年龄/岁 63.60±9.46 54.35±11.13 3.111 0.003 糖尿病史 5(20.0) 0(0) 0.051 二次手术 5(20.0) 1(4.3) 0.191 T分期 0.035 0.852 pT3 6(24.0) 5(21.7) pT4a 19(76.0) 18(78.3) 手术时间/min 239.67±88.43 474.35±140.16 0.000 经口进食时间/d 12.84±3.65 17.3±9.71 2.075 0.047 术后至出院时间/d 15.48±3.78 20.22±10.14 2.11 0.044 手术方式 2.98 0.225 TL 9(36.0) 6(26.1) TL+UND 9(36.0) 5(21.7) TL+BND 7(28.0) 12(52.2) 咽瘘 1(4.0) 6(26.1) 0.044 TL:喉全切除术;UND:单侧颈淋巴结清扫术;BND:双侧颈淋巴结清扫术。 表 2 开放式组与对照组临床资料比较
开放式组 对照组 统计值 P 性别 1.000 男 7(100.0) 22(95.7) 女 0(0) 1(4.3) 年龄/岁 66.71±11.57 54.35±11.13 2.553 0.016 糖尿病史 2(28.6) 0(0) 0.048 二次手术 5(71.4) 1(4.3) 0.001 T分期 1.000 pT3 2(28.6) 5(21.7) pT4a 5(71.4) 18(78.3) 手术时间/min 411.57±141.62 474.35±140.16 0.000 经口进食时间/min 15.43±7.83 17.30±9.71 0.465 0.645 术后至出院时间/d 17.14±7.56 20.22±10.14 0.738 0.466 手术方式 0.211 0.900 TL 2(28.6) 6(26.1) TL+UND 2(28.6) 5(21.7) TL+BND 3(42.9) 12(52.2) 咽瘘 2(28.6) 6(26.1) 1.000 -
[1] Bedrin L, Ginsburg G, Horowitz Z, et al. 25-year experience of using a linear stapler in laryngectomy[J]. Head Neck, 2005, 27(12): 1073-1079. doi: 10.1002/hed.20280
[2] 刘学奎, 李浩, 刘巍巍, 等. 线型闭合器在喉全切除术中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 47(7): 587-590. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2012.07.013
[3] 王文武, 魏小林, 苏纪平. 线型闭合器在全喉切除术中的应用现状[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(1): 78-81. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201701024.htm
[4] Paddle P, Husain I, McHugh L, et al. Outcomes of mechanical stapling for postlaryngectomy open pharyngotomy closure[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(3): 605-610. doi: 10.1002/lary.26208
[5] Mäkitie AA, Niemensivu R, Hero M, et al. Pharyngocutaneous fistula following total laryngectomy: a single institution's 10-year experience[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2006, 263(12): 1127-1130. doi: 10.1007/s00405-006-0152-5
[6] Sofferman RA, Voronetsky I. Use of the linear stapler for pharyngoesophageal closure after total laryngectomy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2000, 110(8): 1406-1409. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200008000-00035
[7] Montoya FS, de Galarreta JCR, del Rey AS, et al. [Comparative study of the use of manual and mechanical suturing in the closure of the mucosaldefect in total laryngectomy] [J]. Acta Otorrinolaringol Esp, 2002, 53(5): 343-350. doi: 10.1016/S0001-6519(02)78319-2
[8] Gonçalves AJ, de Souza JA Jr, Menezes MB, et al. Pharyngocutaneous fistulae following total laryngectomy comparison between manual and mechanical sutures[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 266(11): 1793-1798. doi: 10.1007/s00405-009-0945-4
[9] Calli C, Pinar E, Oncel S. Pharyngocutaneous fistula after total laryngectomy: Less common with mechanical stapler closure[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol, 2011, 120(5): 339-344. doi: 10.1177/000348941112000510
[10] 陈莉莉, 秦照军, 钱芝卫, 等. 线性吻合器在全喉切除术中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(24): 2170-2172. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201524019.htm
[11] 王亮, 王卫卫, 娄卫华. 吻合器全喉切除术与传统方法全喉切除术的临床对比观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(11): 963-966. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201511001.htm
[12] Altissimi G, Frenguelli A. Linear stapler closure of the pharynx during total laryngectomy: a 15-year experience(from closedtechnique to semi-closed technique)[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2007, 27(3): 118-122.
[13] Aires FT, Dedivitis RA, Castro MA, et al. Efficacy of stapler pharyngeal closure after total laryngectomy: A systematic review[J]. Head Neck, 2014, 36(5): 739-742. doi: 10.1002/hed.23326
[14] Shan H, Gao Y, Liu L, et al. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow-band imaging to assist the linear stapler closure of the pharynx during total laryngectomy[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(5): 511-514. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.05.014
[15] Ahsan F, Ah-See KW, Hussain A. Stapled closed technique for laryngectomy and pharyngeal repair[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2008, 122(11): 1245-1248. doi: 10.1017/S0022215108003228
[16] Agrawal A, Schuller DE. Closed laryngectomy using the automatic linear stapling device[J]. Laryngoscope, 2000, 110(8): 1402-1405. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200008000-00034
[17] Ismi O, Unal M, Vayisoglu Y, et al. Stapler Esophageal Closure During Total Laryngectomy[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2017, 28(1): e35-e40. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000003196
[18] Leahy KP, Tufano RP. Primary tracheoesophageal puncture in stapler-assisted total laryngectomy[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2010, 72(2): 124-126. doi: 10.1159/000278257
-




 下载:
下载: