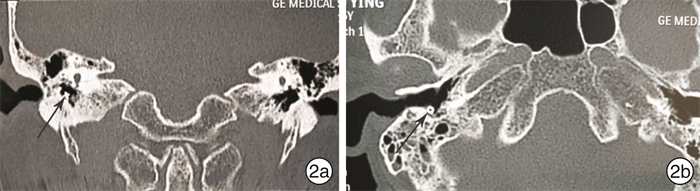
Therapeutic outcome and complication management of grommet insertion for radiotherapy induced otitis media with effusion
-
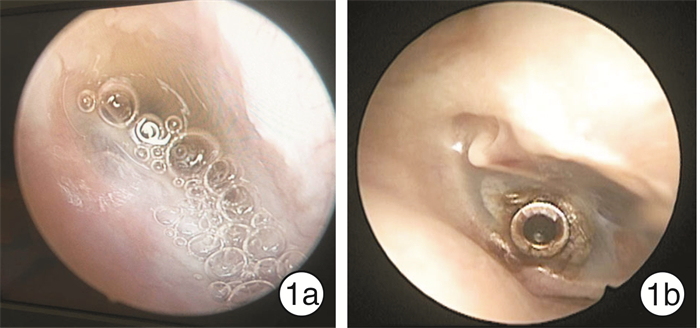
摘要: 目的 评价鼓膜置管术治疗放射性分泌性中耳炎的疗效,分析并发症的原因及其防治方法。方法 回顾性分析实施鼓膜置管术治疗33例(55耳)放射性分泌性中耳炎患者的临床资料。结果 术后7 d复诊,55耳语频听阈均有不同程度提高,平均提高20.79 dB;所有患者耳闷胀感消失,80%的患者耳鸣、头痛症状缓解。术后并发症发生率达67.3%(37/55),包括:通气管脱落11耳(20%),均再次置管;耳漏10耳(18.2%),用抗生素治疗后干耳;通气管阻塞9耳(16.4%),经5%碳酸氢钠滴耳剂治疗后再通;鼓膜内陷粘连4耳(7.3%),行咽鼓管吹张治疗好转;鼓膜穿孔2耳(3.6%),未予处理;通气管内侧移位1耳(1.8%),鼓室手术取出通气管。因并发症或取管后症状发作,行2次以上再置管术31耳(56.4%)。结论 鼓膜置管术治疗放射性分泌性中耳炎,可以改善患者的听力和缓解耳部不适症状,但术后并发症较多,应积极防治,以提高治疗效果。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the therapeutic outcome and complication of grommet insertion for cancer patients in head and neck suffering from otitis media with effusion following radiotherapy.Method Retrospectively analyze the clinical data of grommet insertion in patients with head and neck cancer suffering from otitis media with effusion following radiotherapy.Result Fifty-five ears in 33 cases of cancer patients in head and neck with otitis media with effusion following radiotherapy had been performed grommet insertion. All patients were revisited seven days after operation, the phonetic frequency hearing in 55 ears had been improved in various degrees, and on average, it was increased 20.79 dB compared to that prior to the procedure. Sensation of the ear fullness had been disappeared in all the ears; the symptoms of tinnitus and headache were relieved in 80% of the patients. However, postoperative complications occurred in 67.3%(37/55) of the ears, including: ventilation tube falling out in 11(20%) ears, all of which had been re-catheterized; otorrhea in 10(18.2%) ears, which were healed after antibiotic treatment; Ventilation tube occlusion in 9(16.4%) ears, and they were recanalized after 5% sodium bicarbonate ear drops treatment; tympanic membrane retraction in 4(7.3%) ears, which were restored after eustachian tube blowing; eardrum perforation in 2(3.6%) ears without further treatment; the ventilation tube sliding into the tympanic cavity in 1(1.8%) ear, which was removed by surgery. The grommet was inserted more than twice in 31(56.4%) ears because of complications or recurrence of symptoms after grommet was removed.Conclusion The grommet insertion is used for the treatment of radiotherapy-induced otitis media with effusion, which can improve the hearing and relieve the discomfort symptoms in ear in such patients. However, the incidence of postoperative complications is high and should be actively prevented to improve the therapeutic effect.
-
Key words:
- otitis media, with effusion /
- radiotherapy /
- head and neck neoplasms /
- grommet insertion /
- complication
-

-
[1] Nader ME, Gidley PW. Challenges of hearing rehabilitation after radiation and chemotherapy[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2019, 80(2): 214-224. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1677865
[2] Christensen JG, Wessel I, Gothelf AB, et al. Otitis media with effusion after radiotherapy of the head and neck: a systematic review[J]. Acta Oncol, 2018, 57(8): 1011-1016. doi: 10.1080/0284186X.2018.1468085
[3] Schwarz Y, Manogaran M, Daniel SJ, et al. Ventilation tubes in middle ear effusion post-nasopharyngeal carcinoma radiation: to insert or not?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(12): 2649-2651. doi: 10.1002/lary.26149
[4] Chen CY, Young YH, Hsu WC, et al. Failure of grommet insertion in post-irradiation otitis media with effusion[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2001, 110(8): 746-748. doi: 10.1177/000348940111000809
[5] Young YH, Sheen TS. Preservation of tubal function in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma, post-irradiation[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 1998, 118(2): 280-283. doi: 10.1080/00016489850155026
[6] 唐安州, 周永, 谭颂华, 等. 咽鼓管功能综合检查仪的临床应用初探[J]. 广西医科大学学报, 1999, 16(6): 759-761. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-930X.1999.06.015
[7] Akazawa K, Dio H, Ohta S, et al. Relationgship between eustanchian tube dysfunction and otitis media with effusion in radiotherapy patients[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2018, 132(2): 111-116. doi: 10.1017/S0022215118000014
[8] Kuo CL, Wang MC, Chu CH, et al. New therapeutic strategy for treating otitis media with effusion in postirradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients[J]. J Chin Med Assoc, 2012, 75(7): 329-334. doi: 10.1016/j.jcma.2012.04.016
[9] Charusripan P, Khattiyawittayakum L. The effectiveness of myringotomy and ventilation tube insertion versus observation in post-radiation otitis media with effusion[J]. Eur Arch otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 247(9): 3283-3290.
[10] 周永, 唐安州, 李杰恩, 等. 鼓膜置管治疗鼻咽癌放疗后分泌性中耳炎疗效观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2005, 19(1): 22-23. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200501008.htm
[11] Liang KL, Su MC, Twu CW, et al. Long-term result of management of otitis media with effusion in patients with postirradiated nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2011, 268(2): 213-217. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1381-1
[12] Kisser U, Gurkov R, Louza J, et al. Comparison of characteristics of titanium and fluoroplastic ventilation tubes in adults with healthy middle ears[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2012, 33(6): 983-987. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e318259b70b
[13] Xu YD, Ou YK, Zheng YQ, et al. The treatment for postirradiation otitis media with effusion: a study of three methods[J]. Laryngoscope, 2008, 118(11): 2040-2043. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e31818208d6
[14] Yaman H, Yilmaz S, Alkan N, et al. Shepard grommet tympanostomy tube complications in children with chronic otitis media with effusion[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 267(8): 1221-1224. doi: 10.1007/s00405-010-1220-4
-




 下载:
下载: